In this article, You will know how can a clinical psychologist’s deal with Child’s mental health assessment program and how a child psychologist deals with counseling psychology with psychological assessment tests. A fresher psychologist will know the real meaning of the clinical psychologist’s definition with amazing clinical psychologist child assessment Programs.
Table of Contents
WHAT IS CHILD BEHAVIOR ACCORDING TO CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST?
The characteristics of child behavior are action, reaction, functioning and response to the daily life environment and situation.
MALFUNCTION OF CHILD BEHAVIORS
Child Malfunction or challenging behavior is an impairment with a child’s daily life functioning.
CHILD PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS
According to child psychologist experts from the university of oxford and the University of Pittsburg, the child can be properly valid diagnose at the age of up to 5yrs old. The preschool child behavior problem indicates a problem in the later stage of life, which is creating disturbance s in individuals personal life, family as well as their social life.
The parents should be a concern and distinguish of child normal and abnormal behavior in the early stage of child development life and if they observe any deviate behavior or rapid developmental change as compare to their age group children they should be consulting for assessment to child physician, psychiatrist or expert psychologist.
EARLY CHILDHOOD MAJOR EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOR PROBLEMS
According to DSM-IV criteria underage of 5yrs old child receive a diagnosis of severing behavioral disorders. These may include
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
- Anxiety disorder
- Depression
- Bipolar disorder
- Learning disorders
- Conduct disorders
PARENTING ROLE OF CHILDHOOD SUCCESS
Parents play a major role in treating early childhood behavior issues they can well adjust their behavior.
TYPES OF PARENTING STYLE
- Authoritarian parenting: Strict and rigid rules with no compromise, and no input from the children.
- Authoritative parenting: Strict rules, but parents are willing to listen and cooperate with their children. More of democracy than authoritarian parenting.
- Permissive parenting: Some rules and demands put on children.
- In-home there is no discipline to know, that’s why parents can take apart like a friend in the home.
- Uninvolved parenting: There is not standard Rules to follow and very little interaction. These parents are isolated and can reject or neglect their children.
According to experts, the authoritative parenting style is the most appropriate style for child well-adjusted behavior and happy life.
CAUSES AND EFFECT OF CHILD EMOTIONAL AND BEHAVIOR DISORDERS
- Biological
- Developmental
- Learning pattern
- Home-related environment
BIOLOGICAL: Genetic abnormalities in neurological and biochemical imbalance and brain injury.
BEHAVIORAL FACTORS: lack of adaptive behavior and exposure to maladaptive behavior, exposure to environmental stress.
SOCIAL FACTOR: Destructive family life, rejection of the child by peer group. Over expectation, labeling of child and culture.
PSYCHONALTICAL FACTOR: Traumatic childhood experiences.
READ ALSO: TYPES OF LEARNING DISABILITIES
WHAT IS THE SIGN OF BEHAVIORAL AND EMOTIONAL DISORDER?
The child with the behavioral disorder may acts out the emotional reactions in different situation which will also vary from child to child.
EMOTIONAL SYMPTOMS OF BEHAVIORAL DISORDER

-
Short temper Anger outburst

-
Easily getting annoyed

-
Refusing to follow rules or questioning

-
Difficulty to handle frustration

-
Rebellious behavior

-
Oppositional defiant behavior

CLINICAL CHILD PSYCHOSOCIAL TREATMENT ASSESSMENT
The psychosocial treatment focus on child and parent management strategies, this programmed play an important role in mutual interaction of child, parent’s teacher, and caregivers.
- Set clear and realistic rules
- Clear and simple instruction given to your child according to his or her age
- Improve your child’s social skills through different techniques e.g. storytelling, drawing, etc.
- Help your child to control his anger and emotion through play or drawing
- Build friendship provide a frank environment to the child where they express their feelings and emotion.
- Help your child to be in depended
- Strengthen their social, communication and problem-solving skills through appraisal, unconditional positive regards
- Practice good and positive behavior
- Explain the consequences of disruptive behavior to his child
- Set clear rules and consequences of breaking law and rules
CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST WITH PARENTS MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES
- Set realistic goals
- Respond positively to your child when your child asks for help or attention
- Reduce stress and stay positive interpersonal relationship
- More confidence to tackle the situation or problem-solving
- Better monitor and manage your child behavior
- Learn an effective way of parenting skills
TEACHER ROLE TO MODIFICATION CHILD BEHAVIOR PSYCHOLOGY
- Behavior management in the classroom.
- Improve child social and emotional skills
- Keep Involve the child parents and give them feedback
WHAT IS BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION AND HOW IT WORKS?
Behavior modification is means changing or shaping the behavior of the child through different techniques replaces his or her behavior with the desirable one. The concept of behaviorism its begin in 1938 when B.F skinner published his book the behavior of the organism included four types of principles of operant condition that behavior could be shaped by positive or negative reinforcement.

CLINICAL BEHAVIOR MODIFICATION TECHNIQUES
- Positive reinforcement
- Negative reinforcement
- Positive punishment
- Negative punishment
- Balloon anger management
- Three wishes technique
- Time out
- Response cost
- Time-bound
- Play therapy
- Storytelling
- Reward and Praise for his Good Behavior
POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT
Example: If your child completed their homework they should play favorite video games. e.g. If a child got a good grade in school they will be going for dinner or a park.
NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT
Negative reinforcement refers to unpleasant behave to reinforce good behavior.
Example: Nag your child every day if the child does not throw dust in Bento avoid hearing nag he will use to throw dust in Ben.
POSITIVE PUNISHMENT:
Explain the negative consequences of his negative behavior.
Example: If you do not control your anger or not display anger on positive energy they will be staying outside of the room.
NEGATIVE PUNISHMENT:
In negative punishment taking away something for his misbehaving
Example: If your child has an abusive language or misbehaving, removing him from the activity or not allow them to use a computer or mobile.
CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGIST CONCLUSION:
Behavior modification techniques work in different settings and situations. The parents, teachers, and caregivers can use both positive and negative reinforcement to teach their child behavior modification in an effective way. The teacher should be classroom management through an effective behavior modification plan.
Using the information in this article about emotional and behavior problems and suggestions for behavior modification and self-regulation skills on how to teach children, the student repeated desirable behavior in different situations. Remember to formulate an effective plan and the outcome will be almost effective immediately.
CHILDHOOD ASSESSMENT AND TREATMENT INTERVENTION FOR EMOTION AND BEHAVIORAL DISORDERS:
HOW CAN BE ACHIEVING EARLY INTERVENTION AND ASSESSMENT OF CHILDHOOD?
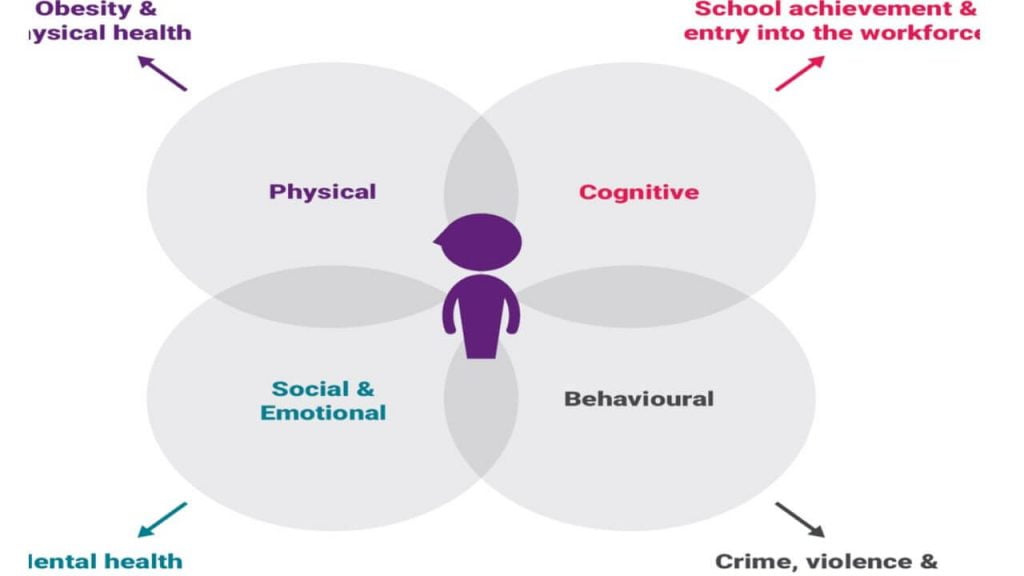
Early childhood assessment approaches focus on four domains which have provided us a comprehensive assessment and help to diagnose childhood. Their physical, Cognitive, behavioral social and emotional development can play a major role throughout the person’s life.
-
Physical development
In physical development focus on early childhood physical health weight, nutrition, using small and large muscles,(fine and gross motor muscles) maturation, presence or absence of any physical disability.
-
Cognitive development
In child cognitive development include early acquisition of speech, language, ability to word produce vocabulary, ability to read and write, communication skill expressive and receptive language e.g.Capability understanding and logical problem solving and their analytical ability.
-
Behavioral development
Includes children’s ability to monitor, self regulates and controls their own behavior. In cognitive development, we can observe the children feeling, actions, responses, and reactions towards the situation.
Children’s positive self-regulatory skills are highly associated with productive relationships with others with their peer group of school as well as school achievement. The child weakens behavioral self-regulation skills are highly risky to children’s involvement in criminals activity during teenage and adulthood.
-
Social and emotional development
In social and emotional development includes awareness emotional need of child .the child recognizes their own emotional needs and the emotional needs of others. Child emotional and social development is also associated with child self-esteem.
Self-respect and manage to their ability to manage their own negative feelings which have promotes the child pro-social behavior with others and reduces the risk of depression and other mental health problems.
Early childhood intervention in the developmental process is also associated highly targets three aspects additional threads to a child development which has adverse outcomes of the child during adolescence and adulthood.
BASIC PSYCHOLOGICAL TESTS USE FOR CHILD BEHAVIORAL AND EMOTIONAL ASSESSMENT BY CLINICAL PSYCHOLOGISTS
|
INSTRUMENT |
TYPES |
AGE |
MINUTES |
| Emotional Early Childhood Scales Emotional Developmental | EMOTIONAL DEVELOPMENT | 5-11 | 30 |
| Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales (VABS) | Developmental | 0-18 | 75 |
| Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-IV) | IQ multitask | 6-16 | 135 |
| Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Functioning (BRIEF) | Nero psychological test | Child and adolescent | 45 |
| Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Test (ADHD) | BEHAVIOR RATING SCALE | 3-13 | 10 |
ARTICLE IS WRITTEN BY ( Clinical Psychologist Najma Ahmad )
Najma Ahmad is one of the best Clinical Psychologist in Mardan and Peshawar with her Professional Career profile by her hard-working in IBADAT HOSPITAL PESHAWAR. she has been working with many senior doctors and well-known hospitals that deal in different conditions related to mental health and Counseling.
EMAIL: [email protected]
Share your Answer with us about how to know if your child feels loved?
READ ALSO: HOW DOES MIGRAINE PAIN OCCURS SYMPTOMS IN BODY










very nice.
its very informative.
Thankyou
Superb Experience
very good